Hello to all lovers homemade, maybe someone had a good dynamic microphone lying around at home, but if it was possible to connect the sound somewhere, it turned out to be very weak in terms of volume, and a makeshift amplifier, which will be discussed in this article, will help to solve this problem.
Before moving on to reading this homemade product, I suggest watching a video that shows the entire assembly process, as well as a small test of it in operation.
In order to make a homemade amplifier for a dynamic microphone, you will need:
* Plastic case, can be ordered by aliexpress
* Soldering iron, solder, flux
* Hot melt adhesive
* Wires
* Boost module
* Dynamic microphone
* 6.3mm microphone jacks and micro usb
* Microphone for video surveillance, a reference to
* Device for soldering "third hand"
* Heat-shrink tubing
That's all it takes to make an amplifier. do it yourself.
Step one.
First of all, you need to wait for the parcel from China, after which this microphone for video surveillance needs to be disassembled, namely, remove the capsules themselves and release the amplifier from the factory shrink. Then we take two wires and solder them to the microphone installation site using a soldering iron with a small sting, we also solder two wires, but already to the power supply, since power will be provided from 12 volts and from 5 volts.
Step Two
Solder the wires coming from connecting the microphone to the 6.3mm jack, it will use the two lower pins.
After this, it is necessary to protect the amplifier board so as not to damage its small components during operation, it will be most convenient to do this with the help of a heat shrink tube, we put it on the amplifier, threading the wires in advance and crimping it, conducting it at a distance with a lighter or a blowtorch. For this procedure, it was necessary to re-solder, and then solder the wires, so be careful.
Step Three
There are two freely sticking wires in the air, they are responsible for power from a current source with 5 volts at the output, in fact this is any charging unit for the phone. But since the amplifier board runs from 12 volts, it is necessary to increase 5 volts from the power supply to 12 working ones, so a converter is needed for this.
This converter can be found on the open spaces of aliexpress at a very low price, it must be soldered to the micro-connector with a soldering iron and wires, after soldering, fill the contacts with hot glue so that there is no short circuit.
Then you need to connect the power supply from any phone and adjust the trimming resistor on the boost module so that the output voltage is 12 volts.
After the converter is adjusted to the desired voltage, it can be soldered to the power wires of the amplifier, which were previously soldered.
Step Four
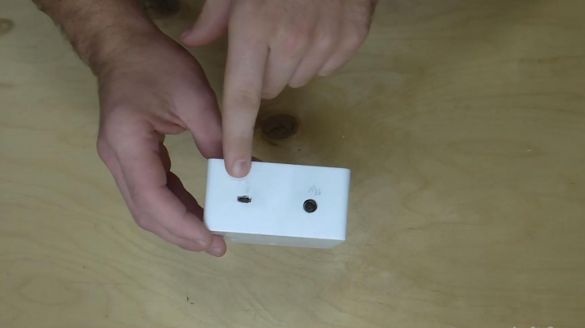
Now you need to install everything in the case, which can also be purchased in China or the radio store.
In it, we drill holes for the 12-volt power jacks, connecting a 6.3 mm microphone, micro-usb port for power from 5 volts and a tulip. Using a screwdriver and a drill installed in it, we make a pair of holes for the sockets, for a 6.3 mm socket, the hole for the fastener needs about 10 mm, if necessary, you can adjust everything with a scalpel or clerical knife.
All the sockets are glued inside the case to hot-melt adhesive, if there is no thermal gun, then any heater will help here, be it a lighter or a soldering iron.
Step Five
After all the manipulations, you can check the operation of the device, connect the power to the amplifier and the plug of the dynamic microphone, and the recorder is already on the tulip, as a result we get a fairly good and loud sound than without the amplifier, so if you have sound recorded at a low volume, I advise you to do imagine this amplifier that will fix this problem.
On the case, a 5 volt power supply is connected here.
And the output of the amplified sound to the tulip, which can be connected to any recording device.
That's all for me, thank you all for your attention and creative success.