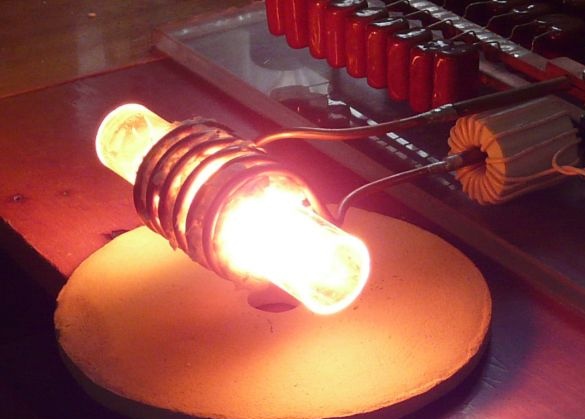
The principle of operation of an induction heater is based on two physical effects: the first is that when a conductive circuit moves in a magnetic field, an induced current arises in the conductor, and the second is based on the release of heat by metals through which current is passed. The first induction heater was implemented in 1900, when a method for contactless heating of the conductor was found - for this, high-frequency currents were used, which were induced using an alternating magnetic field.
Induction heating has found application in various fields of human activity due to:
quick warm up;
the ability to work in environments with different physical properties (gas, liquid, vacuum);
lack of pollution by combustion products;
the possibility of selective heating;
shapes and sizes of the inductor - they can be any;
process automation capabilities;
high percentage of efficiency - up to 99%;
environmental friendliness - no harmful emissions into the atmosphere;
long service life.