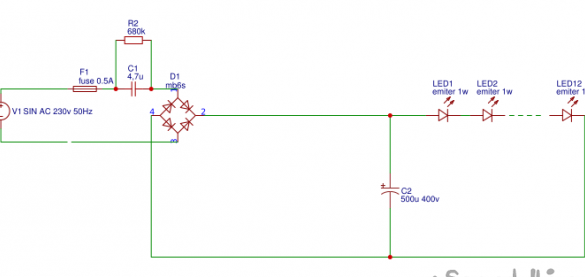
Let's start with the analysis of the classical circuit with a ballast capacitor. The ballast capacitor C1, being a current source, having received voltage from the fuse F1 and the limiting resistor R1, which is designed to protect the ballast from the inrush current when it is switched on for the first time, limits the current, and the direct current source rectified by the diode bridge D1 is directed to the led1-led12 LED circuit. The advantages of this scheme are simplicity, accessibility of parts, not afraid of KZ at the output. But there are significant drawbacks: 1. The presence of pulsations of 100 Hz at the output of the filtering capacitor, which, however, can be removed by increasing the capacity of the filtering capacitor C2 to 500 μf, since after the diode bridge the voltage amplitude reaches up to 310 volts, then the filtering capacitor must withstand this voltage, select it plus some margin, away from sin, let it be 400 volts, and now imagine what its dimensions will be.
The following two points of the disadvantages of this scheme follow from this.
2. Dimensions of the filtering capacitor.
3. The high cost of a filtering capacitor with such parameters.
And usually hams compromise, either put a filter capacitor with a lower capacity, but at a high voltage, or given the fact that when connected
ice of the chain there is a voltage drop equal to the sum of the voltages of all ice elements which is subtracted from the input voltage in front of the ice chain, this voltage plus some margin and the voltage of the filtering capacitor C2 is selected.
Which seems to save the situation but is a bad and even dangerous decision, since when one of the LEDs is burned, a chain of series-connected LEDs is disconnected from the source, and as a result, the voltage on the filtering capacitor rises sharply to a value of 310 volts, and since the electrolytic the capacitor becomes the load itself, begins to boil and can fail, causing an emergency with bad consequences. The above is the fourth drawback and all of the above crosses out the simplicity and cheapness of the scheme ... But thanks to A. KARPACHEV, from Zheleznogorsk, Kursk region. he figured out how to get around this, and created a circuit that protects the filtering capacitor from overvoltage, and the protection works when the ballast capacitor is burned and shorted, and the circuit allows you to apply lower voltage to the LED circuit, and as a result choose a smaller capacitor , which will reduce the dimensions of the device itself and also choose a large filter capacitor C2
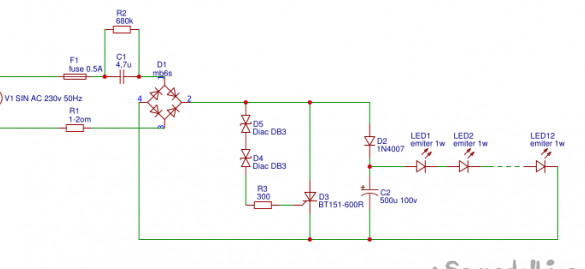
The essence of the circuit is that the mains voltage passing through the limiting resistor R1 and the fuse F1 gets to the Ballast capacitor C1, is limited by current, then rectified by the diode bridge D1, then it goes to the diode D2 through which the capacitor C2, in turn, is charged, at the same time the moment when the voltage at the input of the dynistors D4-D5 increases to the breakdown voltage of the dynistors, the thyristor will open briefly and short-circuit the diode D2 and capacitor C2, due to which the capacitor will begin to discharge while s are closed to the breakdown voltage, in fact we get a kind of stabilization and protection of the filter capacitor overvoltage if, for any reason disappear load, that is, one of the LEDs will burn, or burn the ballast capacitor. Referring to the description of the DB3 parameters, its breakdown voltage is 28-32 volts, in a 10-watt led lamp I used a chain of 12 1-watt LEDs, then the voltage of 32 volts is clearly not enough for me, and therefore I put two dinistors in series, raising the breakdown voltage to 61 volts. Since I bought LEDs from China, I decided not to overload them, and I swung the LEDs to 0.7-0.8 watts, choosing a ballast capacitor capacity of 4.3-4.7 microfarads. The capacity of the ballast capacitor can be calculated as follows, we multiply the capacity of the ballast by 0.051 ml and accordingly we obtain the output current (in general, we need to multiply by 0.065, but these 0.051 ml were empirically determined, to see 0.014 ml takes on the protective circuit from the diac and thyristor, but we do not greedy, let them eat), the LEDs are good, they shine brightly, that is, they give out their declared 100 lumens. The vd2 diode protects the dynistor input from a voltage surge when the thyristor is closed, while locking securely.
According to the author’s recommendation, the limiting resistor R1 needs to be placed in an insulating tube made of fiberglass, choose a Ballast capacitor K73-17 at 630 volts, I used Chinese Cbb 3.3 microfarads at 630 volts +1 microfarads at 630 volts, it turns out cheaper, the thyristor must withstand no less 10 amperes and also a voltage of at least 300 volts, so I chose bt151 r600, even the bt139 triac can come up, which of course is wasteful, but I didn’t have a thyristor and I used a triac, in this inclusion it is also suitable. That's all, thank you for your attention and successful finds and assemblies. Thanks again to the author of this scheme, and in general I strongly recommend that you read his article, he has described everything more meticulous and competent, my modest goal is to popularize his scheme, which I really liked ...