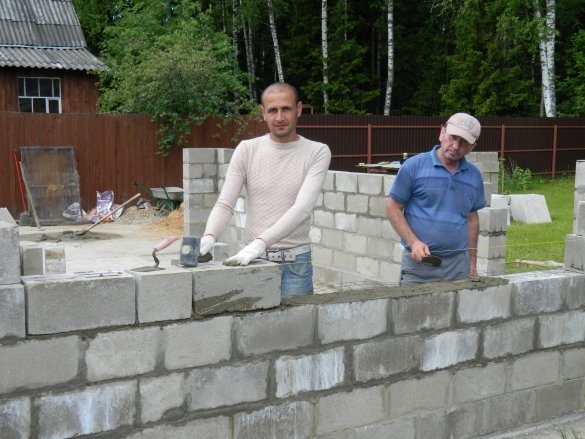
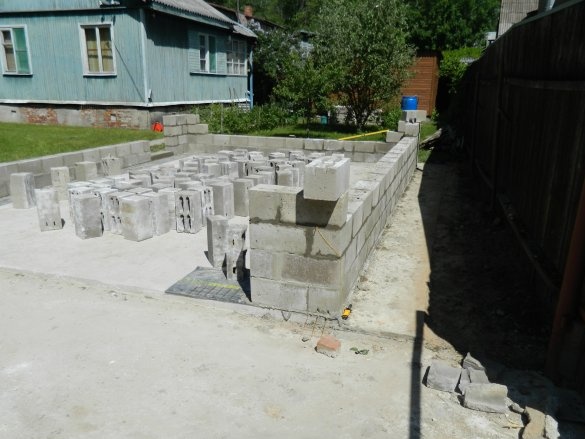
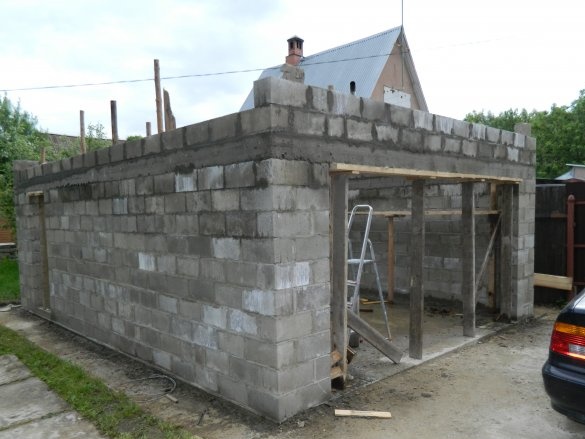
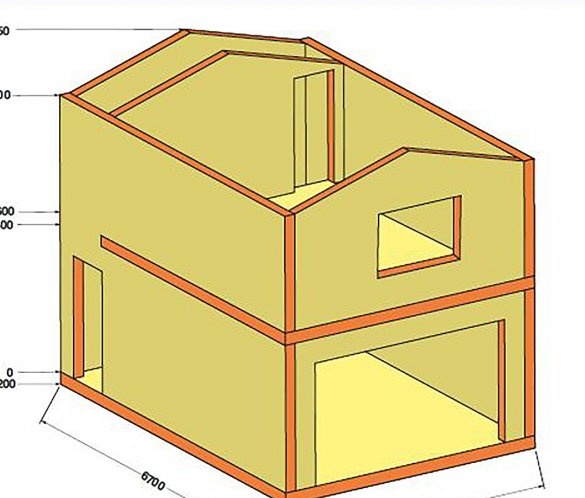
Winter passed, the foundation had to stand. It's time to start building. As I decided, the bottom the garage I will make from slotted sand-cement blocks, and the living room upstairs from foam concrete. I decided to put the staircase inside. The general plan of the garage is presented.
Read about the foundation production in the first part.
Why foam concrete blocks are good, that they have poor thermal conductivity (thermal conductivity coefficient 0.13-0.14 Kcal / m² * deg.), When compared with aerated concrete. This is approximately 4 bricks. They do not absorb water, as their pores are closed and light in weight. In terms of the size of the standard block (foam concrete blocks are usually larger), it weighs about 12 kg. But they have very poor adhesion to plaster. But this problem is solved - a small amount of the cheapest liquid soap is added to the plaster solution.
First, it is necessary to concrete the blind area to a width of 500 mm from the perimeter of the foundation with a thickness of 100 mm with a reinforcing mesh. Concrete was poured into a pre-prepared trench with a sand cushion covered with geotextiles and a laid reinforcing mesh. Concrete was interfered by hand in a large trough. Then, paving slabs measuring 500x500x45 mm with a slight slope outward will lie on the blind area.
The four-slit sand cement block has dimensions of 188x190x390 mm and a weight of 21 kg. The blocks were laid on a ready-mixed mortar of cement grade M500.
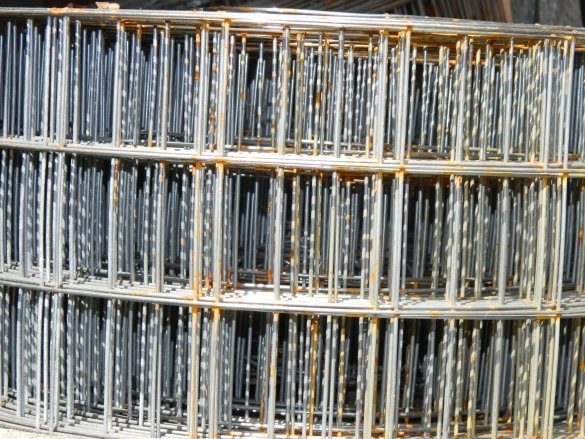
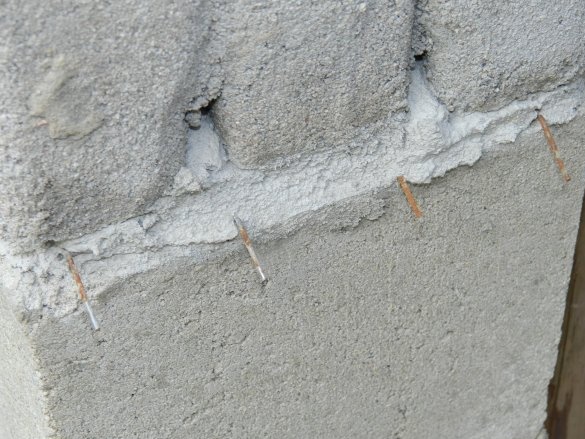
Under the first row of blocks, a hydroisol and a reinforcing 4 mm mesh were laid in two layers, then a rolled 1.5 mm mesh was laid through every two rows of blocks.
The formwork was made and concrete was filled with sills for the front door with a height of 100 mm.
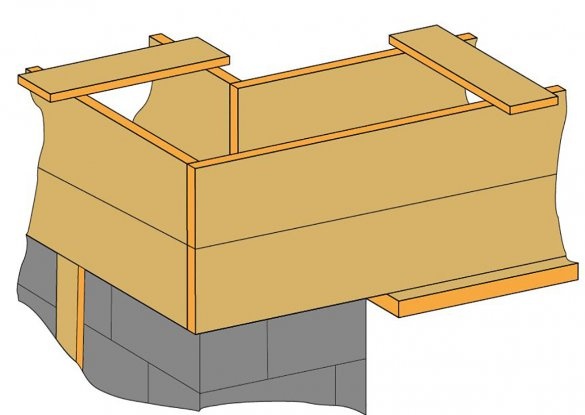
It is worth telling in detail about the preparation of formwork for the AWP belt.
The side formwork panels were made of two boards with a section of 40x100 mm. From the sides they are sewn by scraps of boards with a cross section of 25x120 mm through about 1500 mm. In the corners they were sewn with screws in a single box. Where there should have been openings for the gate and front door, two boards with a section of 40x120 mm were used, which are attached to the side shields from below. In the openings, columns are installed as props. After the reinforcing assemblies were placed inside the formwork and connected together in the corners by knitting wire, trimmed boards were packed along the upper edge of the formwork to prevent it from diverging when pouring. To eliminate the divergence of the side shields from below, they are interconnected by steel wire.On the walls, where there were no openings, the formwork is propped up by boards at the level of the bottom of the fill.
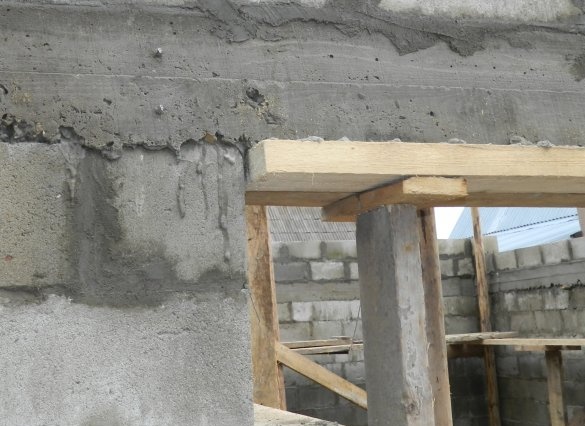
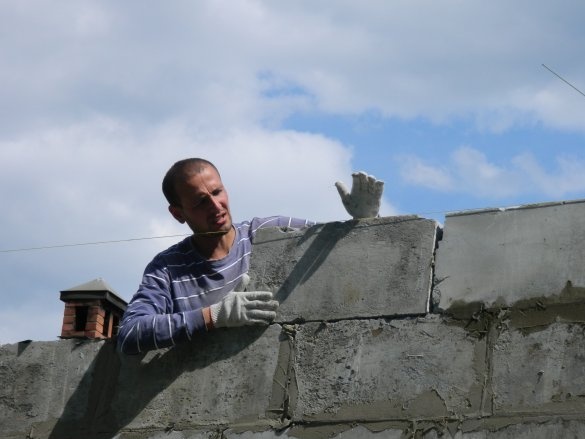
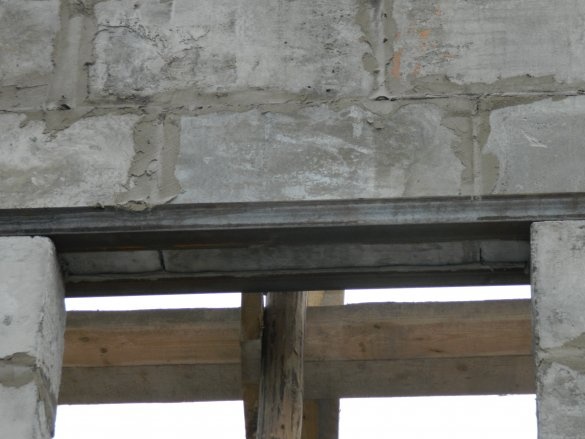
At a masonry height of 2000 mm around the garage perimeter, a continuous arm with a 12-mm reinforcement was connected, connected in the form of a box of 4 bars, and hexagonal 6 bars above the entrance gate,
section of 200x200 mm. At the same time, the arm belt formed the top of the gate and door openings.
After the concrete has hardened, the masonry height is brought up to 2400 mm by sand-cement blocks.
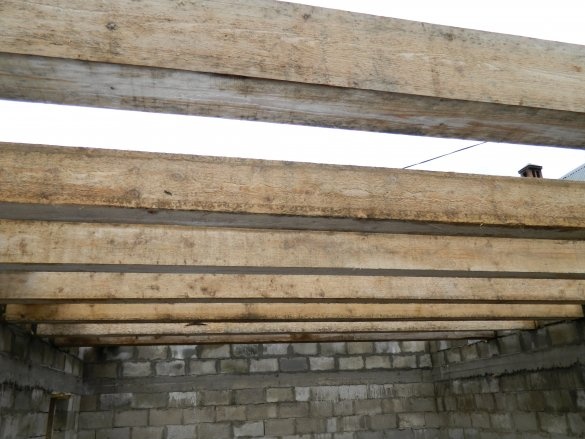
and from the gate to the front door, floor beams are laid through 500 mm. Since the span is quite large, we used a beam of 150x200x5000 mm lying on the wide side. The extreme beam on which the partition for the second floor will be built has a section of 200x200 mm.
The gaps between the beams are also filled with the same blocks. Where the beams are in contact with the blocks, a hydroisol is laid. A ceiling of 400 mm, formed above the opening for the gate, is enough to install a sectional lifting gate in the future.
Foam concrete blocks measuring 200x300x600 mm were fixed with special glue for aerated concrete.
At a distance of 900 mm from the top of the beams, an opening with a width and height of 900 mm was left on the facade for the window. At a masonry height of 4400 mm, a Mauerlat from boards with a cross section of 50x200 mm was fixed using anchor bolts ø12x300 mm at the upper ends of the side walls. with preliminary insulation with hydroisol between it and foam concrete.
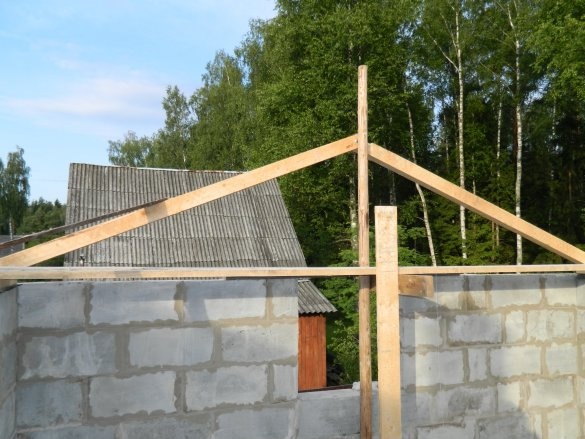
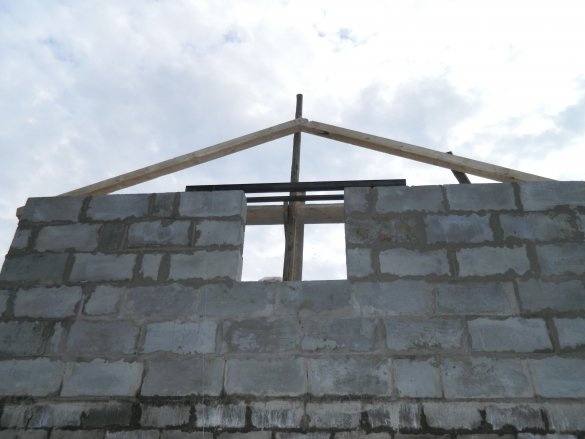
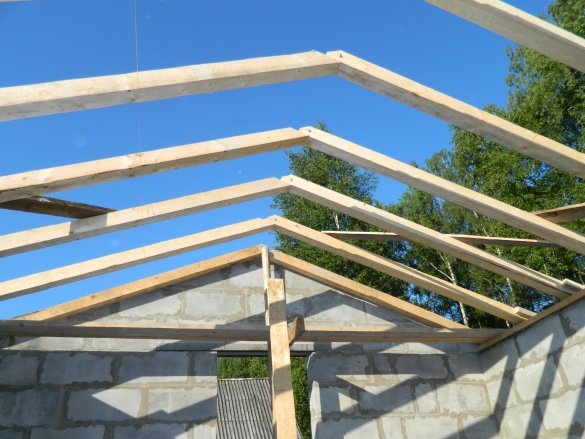
For the brood of pediments from a beam with a section of 100x100x6000 mm, the side rafters are installed, which are installed inside the masonry.
At the top of the opening where the window should be, two 63-mm angles with a length of 2000 mm are installed, which are welded together by a strip along the width of the block. Pediments brought to a height of 5450 mm along the upper end of the rafters.
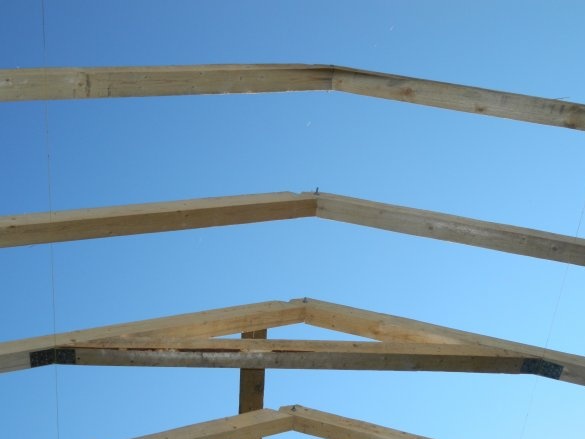
A lace is stretched between the extreme rafters along the ridge of the future roof, and the remaining rafters are installed from the 100x100x6000 mm timber. Where the living area will be located, between the rafters a distance of 500 mm. Where there will be a staircase and a platform for entering the second floor - 600 mm.
At a height of 2480 mm, rafters were installed cross-members from a bar of the same section. They were fastened with steel corners.
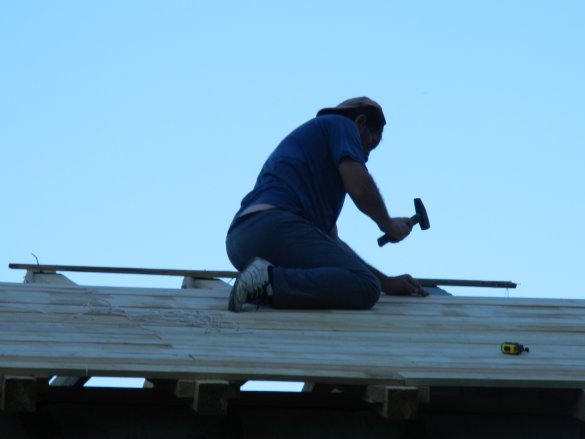
The crate must be made continuous, since the roof will have to be insulated. For it, an edged board of 25x120x6000 mm was used. She was sewn to the rafters with a release of 300 mm around the perimeter of the roof.
Ruberoid is shot to the crate by a stapler. Two layers were laid: along and across the roof slopes.
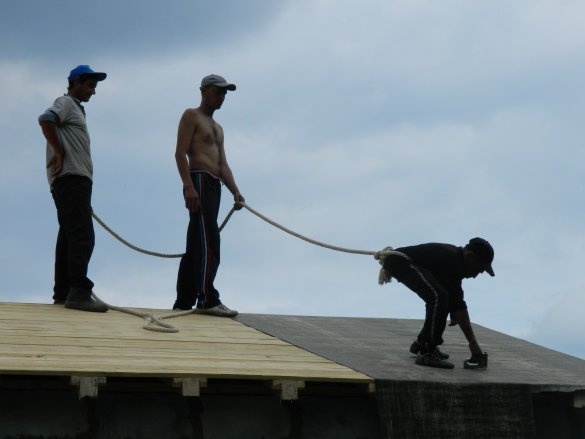
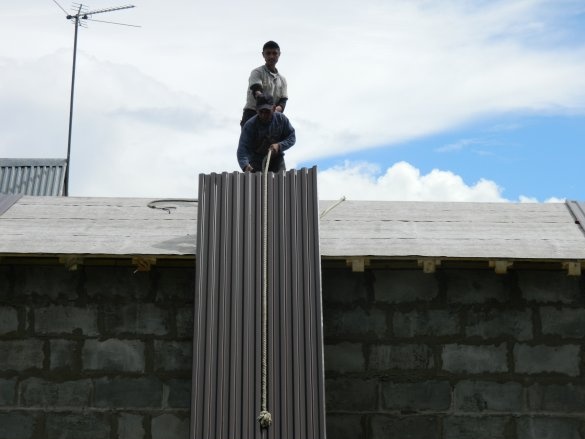
Further on the roof was laid professional sheet # 21 (equal wave) color 8017 (brown) 3000 mm long with a working width of 1050 mm. It took 16 sheets (8 for each slope of the roof). For fastening the sheets, special roofing screws ø4.8x35 mm were required. The skate is fixed on roofing screws ø4.8x70 mm.
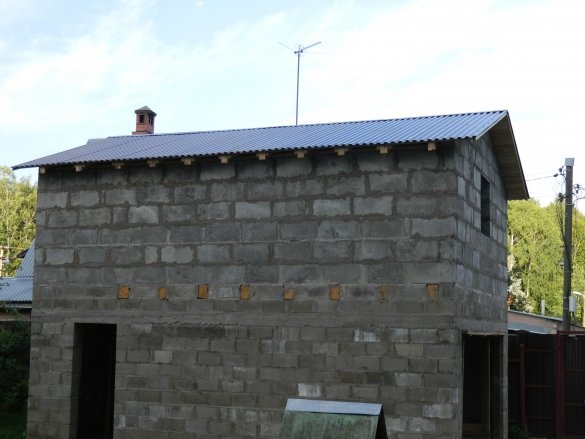
In black we have a built garage.
It remains a little: to plaster the walls inside and out, lay out the tiles on the garage floor, finish the blind area, put the gate and door, order and put up the window, make the stairs to the second floor and, most importantly, go into the second floor.
I spent about 270,000 rubles in money. The most basic price fell on the blocks, their delivery and on hired labor.
My advice: draw everything (block to block) on paper, estimate your strength, that is, what you can, do it yourself (do not hire workers). Hire only for heavy work - knead concrete, lay blocks, etc.