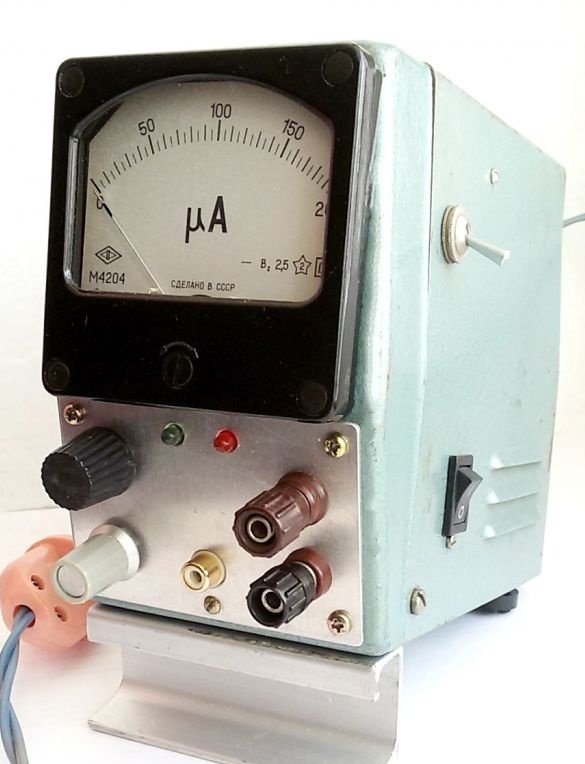
When setting up various electronic devices requires a power supply unit (PSU), in which there is an adjustment of the output voltage and the ability to control the level of operation of the protection against overcurrent over a wide range. When the protection is activated, the load (connected device) should be automatically disconnected.
A search on the Internet gave several suitable power supply circuits. He stopped at one of them. The circuit is easy to manufacture and commission, consists of accessible parts, fulfills the stated requirements.
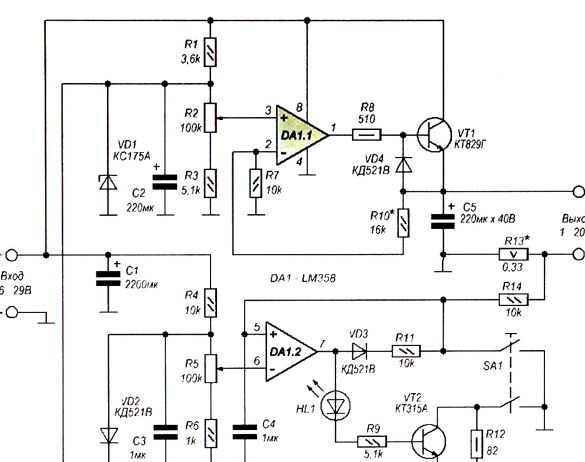
The power supply proposed for manufacture is based on the operational amplifier LM358 and has the following characteristics:
Input voltage, V - 24 ... 29
Output stabilized voltage, V - 1 ... 20 (27)
Protection operation current, A - 0.03 ... 2.0
Photo 2. Power supply circuit
An adjustable voltage regulator is assembled on an operational amplifier DA1.1. The amplifier input (terminal 3) receives the model voltage from the engine of the variable resistor R2, the zener diode VD1 is responsible for its stability, and the voltage is supplied to the inverting input (terminal 2) from the emitter of the transistor VT1 through the voltage divider R10R7. Using a variable resistor R2, you can change the output voltage of the PSU.
The overcurrent protection unit is made on the operational amplifier DA1.2, it compares the voltage at the inputs of the op-amp. Input 5 through resistor R14 receives voltage from the load current sensor - resistor R13. The inverting input (pin 6) receives an exemplary voltage, for the stability of which the VD2 diode with a stabilization voltage of about 0.6 V is responsible.
While the voltage drop created by the load current on the resistor R13 is less than the exemplary, the output voltage (pin 7) of the DA1.2 op amp is close to zero. In the event that the load current exceeds the permissible set level, the voltage at the current sensor will increase and the voltage at the output of the op amp DA1.2 will increase almost to the supply voltage. In this case, the HL1 LED turns on, signaling the excess, the transistor VT2 opens, bypassing the Zener diode VD1 with the resistor R12. As a result, the transistor VT1 closes, the output voltage of the PSU decreases almost to zero and the load switches off. To turn on the load, press the button SA1. The protection level is adjusted using a variable resistor R5.
BP manufacturing
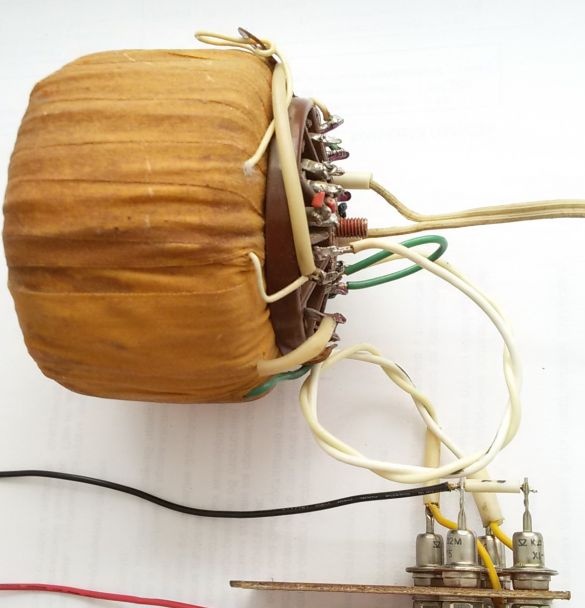
1. The basis of the power supply, its output characteristics are determined by the current source - the used transformer. In my case, a toroidal transformer from a washing machine was used. The transformer has two output windings on 8v and 15v. By combining both windings in series and adding a rectifier bridge on the KD202M medium power diodes at hand, I got a DC voltage source 23v, 2a for a power supply.
Photo 3. Transformer and rectifier bridge.
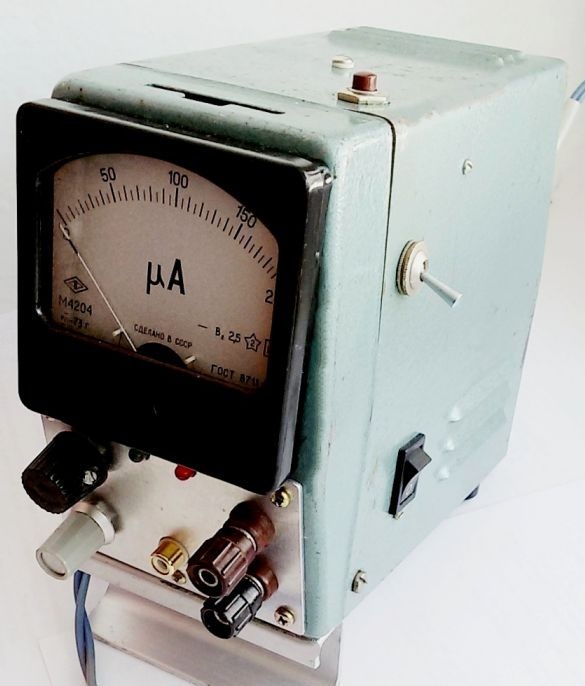
2. Another determining part of the PSU is the instrument body. In this case, a children's slide projector interfering in the garage. Having removed the excess and having processed in the front of the hole to install the indicating microammeter, we obtained a blank for the PSU case.
Photo 4. BP case blank
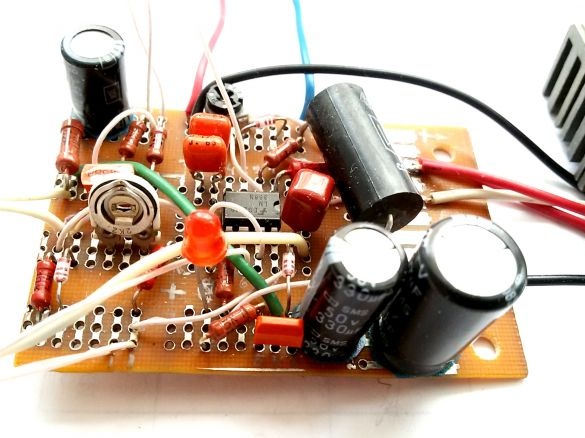
3. The electronic circuit was mounted on a universal mounting plate measuring 45 x 65 mm. The layout of the parts on the board depends on the dimensions found in the component farm. Instead of resistors R6 (setting the operating current) and R10 (limiting the maximum output voltage), trim tab resistors with a 1.5 times larger nominal value are installed on the board. At the end of the PSU settings, they can be replaced by permanent ones.
Photo 5. Mounting plate
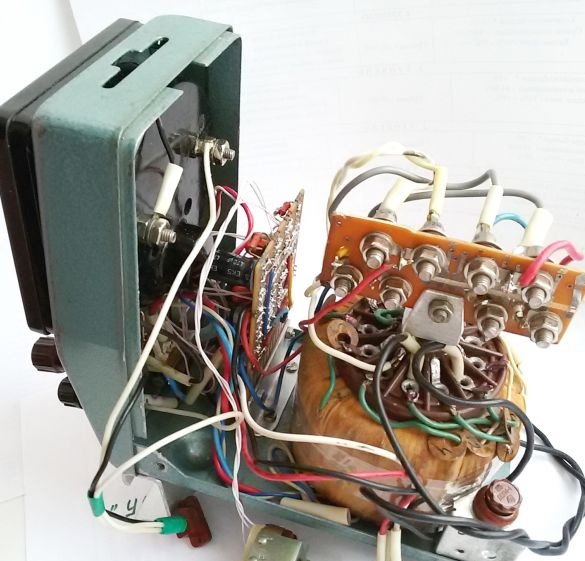
4. The assembly of the circuit board and external elements of the electronic circuit in full for testing, tuning and adjusting the output parameters.
Photo 6. PSU control unit
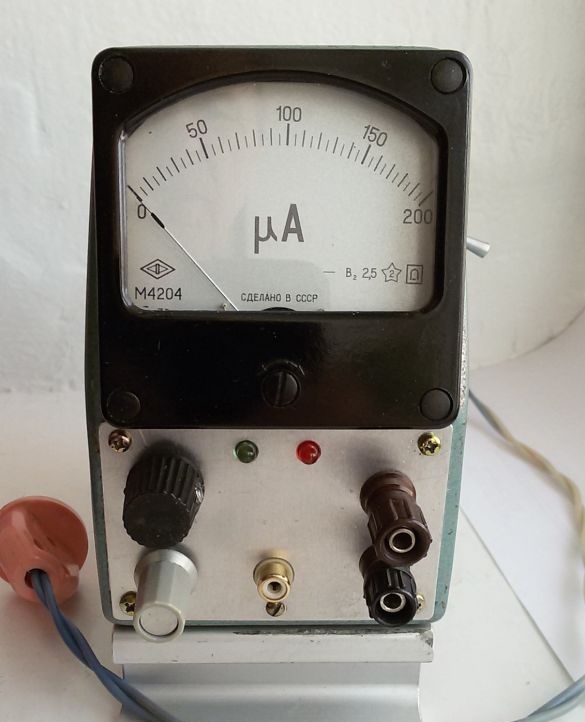
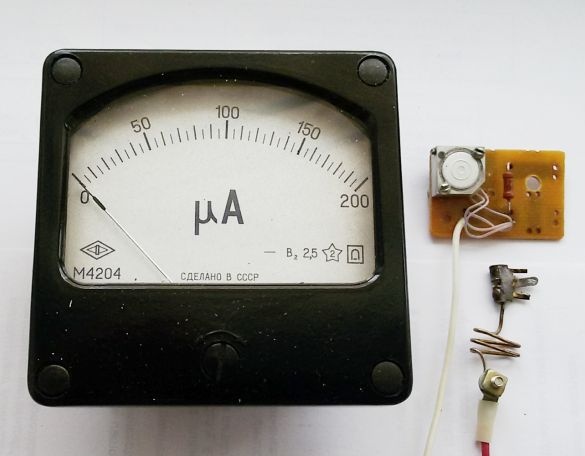
5. Fabrication and adjustment of the shunt and additional resistance to use a microammeter as an ammeter or a BP voltmeter. Additional resistance consists of series-connected constant and tuning resistors (pictured above). A shunt (pictured below) is included in the main current circuit and consists of a wire with low resistance. The wire cross section is determined by the maximum output current. When measuring the current strength, the device is connected parallel to the shunt.
Photo 7. Microammeter, shunt and additional resistance
Adjustment of the length of the shunt and the value of the additional resistance is carried out with an appropriate connection to the device with monitoring for compliance with a multimeter. Switching the device to the Ammeter / Voltmeter mode is performed by the toggle switch in accordance with the scheme:
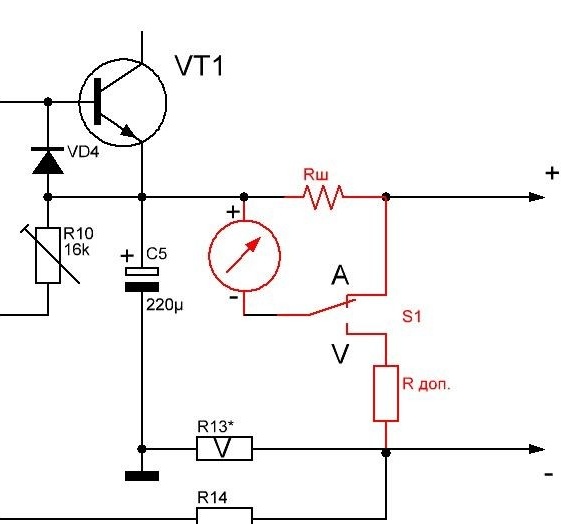
Photo 8. Scheme of switching the control mode
6. Marking and processing of the front panel of the PSU, installation of remote parts. In this embodiment, a microammeter is placed on the front panel (toggle switch for A / V control mode to the right of the device), output terminals, voltage and current regulators, operation mode indicators. To reduce losses and in connection with frequent use, a separate stabilized 5-volt output is additionally output. For this, the voltage from the transformer winding to 8V is supplied to the second rectifier bridge and a typical circuit at 7805 with built-in protection.
Photo 9. Front panel
7. Assembly of the power supply. All power supply elements are installed in the housing. In this embodiment, the radiator of the control transistor VT1 is an aluminum plate 5 mm thick, mounted in the upper part of the housing cover, which serves as an additional radiator. The transistor is mounted on the radiator through an electrically insulating gasket.
Photo 10. Assembling a PSU without a cover
Photo 11. General view of the power supply.
Details:
The operational amplifier LM358N incorporates two op-amps.
Transistor VT1 can be replaced with any of the series КТ827, КТ829. Transistor VT2 any of the KT315 series. The Zener diode VD1 can be used by anyone with a stabilization voltage of 6.8 ... 8.0V and a current of 3 ... 8 mA. VD2-VD4 diodes from the KD521 or KD522B series. Capacitors C3, C4 - film or ceramic. Oxide capacitors: C1 - K50-18 or similar imported, the rest - from the K50-35 series. Fixed resistors of the MLT series, variables - SP3-9a.
Establishing a power supply - the variable resistor R2 engine is moved to the upper position according to the scheme and the maximum output voltage is measured, set to 20 V, selecting resistor R10. After that, the load is connected to the output and measurements of the protection operation current are made. To reduce the level of protection operation, reduce the resistance of the resistor R6. To increase the maximum level of protection operation, reduce the resistance of the resistor R13 - load current sensor.