Before every car owner someday the question arises of how to charge a run down battery. He also appeared in front of me once. And it happened, as always unexpectedly, on a day off, in the village, and as luck would have it, nobody nearby found anything like charging. I had to strain the gyrus and quickly make a simple but powerful charger out of the available tools. And the burnt UPS helped me in this - an uninterruptible power supply for computers. Without going into deep details, I just note that this device powers the computer from the built-in 12-volt battery in case of power failure.
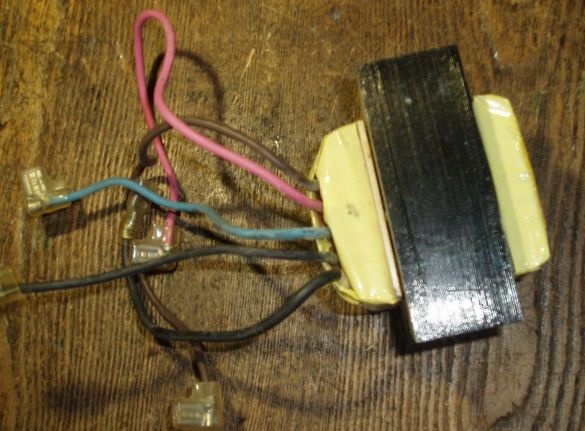
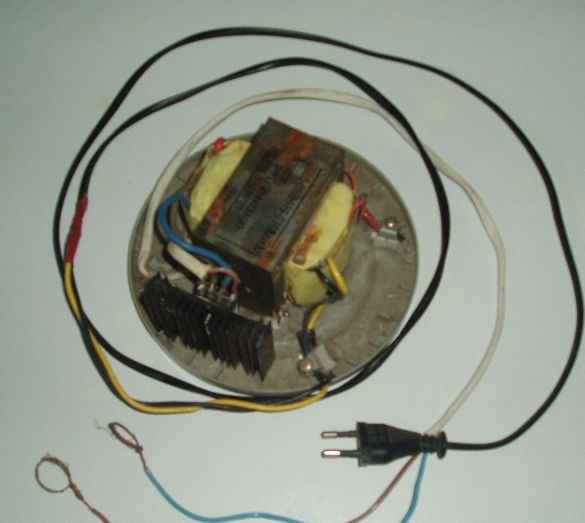
The most important thing is taken from the broken uninterruptible power supply - a powerful transformer, which usually remains intact, we do not need all other spare parts from it.

So, to make a simple charger you will need:
1. Transformer from a burnt down uninterruptible
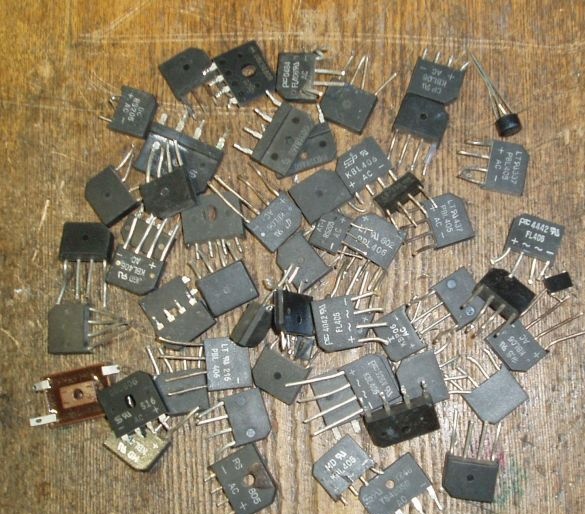
2. Diode bridge (rectifier) 2-4 pcs.
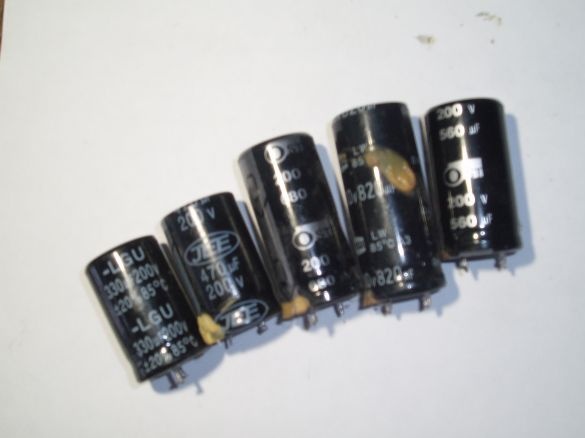
3. Capacitor 100 ... 1000 microfarads with a voltage of at least 25 V
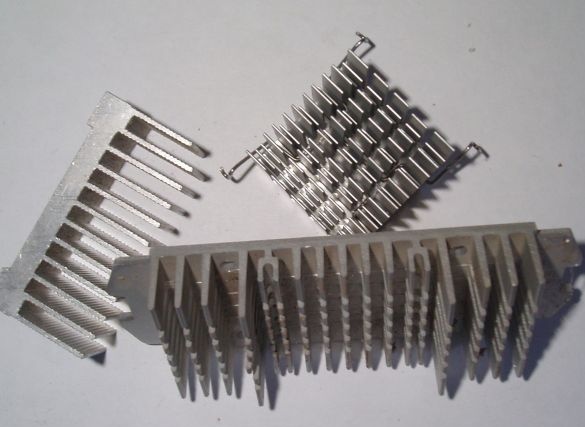
4. Medium-sized radiator
5. Board, plywood, plastic
6. Thermal grease KPT-8
7. Tester
8. Soldering iron, pieces of wire
Using a tester, we determine the conclusions of the winding that have greater resistance (from 10 to 50 Ohms), it will be a 220 V network winding. The outputs of the secondary winding are 12V thicker, it is wound with a thicker wire, so the resistance of the secondary winding is almost zero.
The conclusions that went to the output connectors of the uninterruptible power supply will now be connected to the network, and the wires through which 12V was connected from the board will be connected to the rectifier.
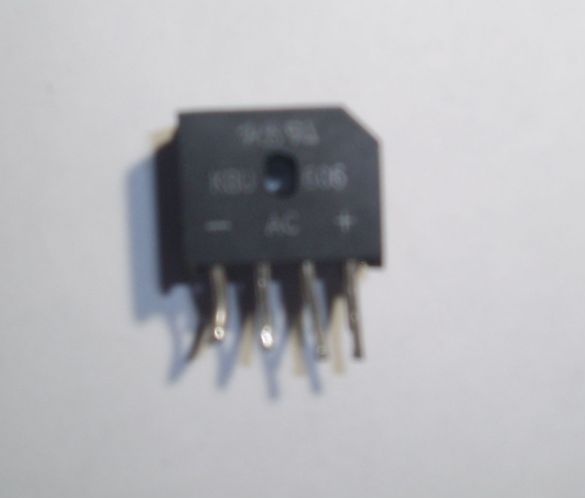
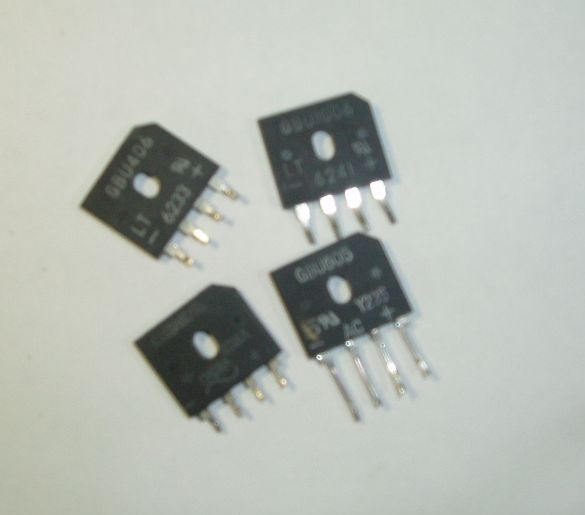
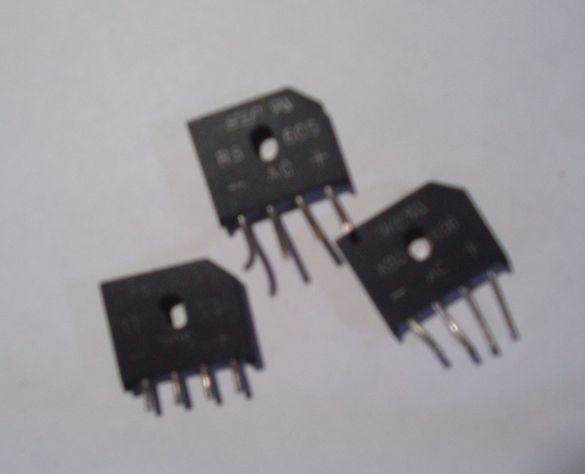
Still need a few rectifier diode bridges GBU406, GBU 605, GBU606, and a filter capacity, a capacitor from 100 to 1000 microfarads for a voltage of at least 25V (from a burned-out computer power supply). A small heatsink for diodes will also come in handy. Of course, you can make a rectifier on ordinary diodes with a maximum current of at least 10 A and a reverse voltage of at least 25 V, but at that moment they were not at hand, and subsequently I also used ready-made rectifier bridges, because they are conveniently mounted on a radiator . The rectifier bridges are stacked, smeared with heat-conducting paste and pressed against the radiator with a long bolt. All leads of the same name are connected in parallel. Pros with pluses, minuses with minuses, etc.
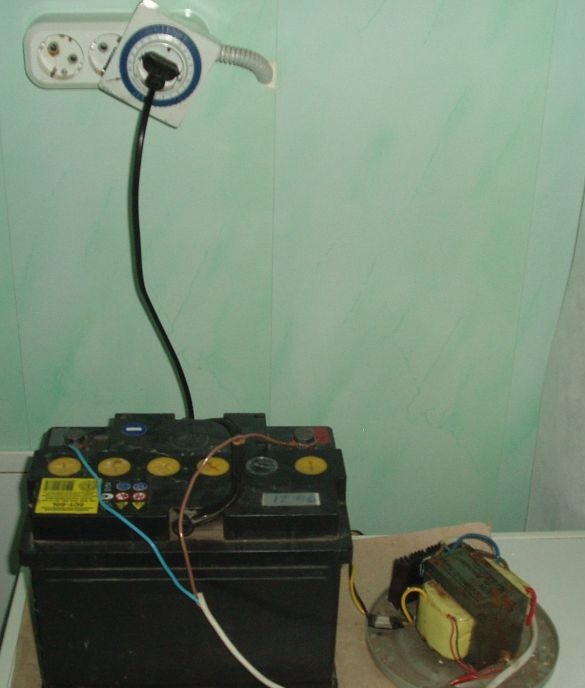
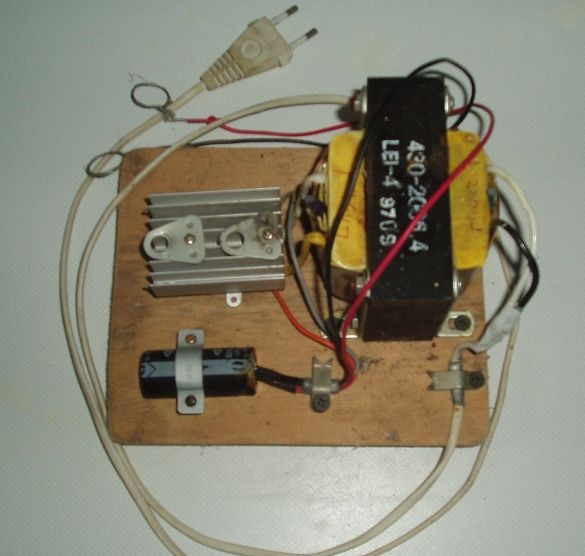
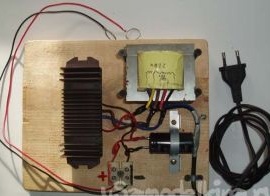
A transformer, a radiator with diodes are mounted on a suitable wooden plank, plywood, or piece of plastic, the entire circuit is mounted, the cord with the plug from the old soldering iron is connected - and the charging is ready!
Mounting options and layout of the charger units can be any, based on what is at hand.
With a rectified output voltage of about 18 V, the charger freely gives a current of up to 5 A. An ordinary battery charges in an hour, a heavily charged battery in 3 ... 4 hours. Many motorists in our village now have such a charge.
Moreover, for a better battery charge, I came up with a charger, in pulse mode. The pulse of course, loudly said, this only means that it is connected to the outlet through an electromechanical time switch.
This is a simple diurnal electromechanical relay, originally from the Middle Kingdom, they sell 150 rubles at a store.


On the disk, you can set the time when it will be turned on, and when off. I chose the mode when it turns on for 15 minutes, and it is turned off for 15 minutes.
So it turns out that the battery is charged in periods of 15 minutes with a powerful current, and then the electrolyte settles for 15 minutes.
During the night, the device charges the battery perfectly, and its service life thus extends very significantly.