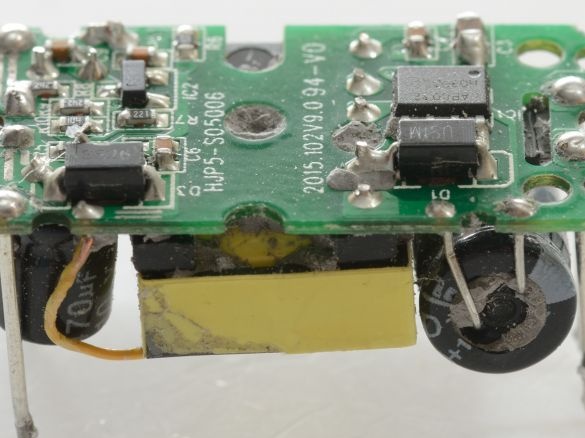
For anyone electronic the device needs power, if it requires energy 24 hours a day, then its best source will be the electric network. Here the choice usually stands between the so-called capacitor power supply and switching power supply. I propose using the second option, since modern UPSs with very small sizes and masses (this weighs 18 g) can convert a high AC voltage into a small DC voltage with minimal losses. China offers us miniature AC-DC converters with an output power of 3 W at a voltage of 5 V, which will be especially important for your projects on microcontrollers.
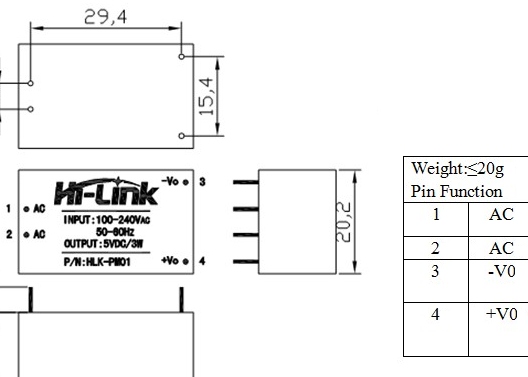
Specifications:
Small overall dimensions, easy
Input voltage 90-264 VAC
Low ripple output
There is a short circuit protection
High device efficiency
Loss without load less than 100 mW
Operating temperature: -20 - +60
Ambient temperature: up to 40 C
Relative humidity: 5-95%
Cooling Type: Passive
Electrical Specifications:
Rated Input Voltage: 100-100 VAc
Input Voltage Range: 90-90 VAc
Maximum input current: 0.2 or less.
Input surge current: 10 or less.
Maximum input voltage: 270 or less VAC
Input soft start: 50 or less MS
Efficiency at low input voltage: Vin = 110 VAC, efficiency 69% and more
High input voltage: Vin = 220 VAC, efficiency 70% or more
Service life: MTBF of at least 100,000 hours
Rated idling output voltage: + 5 + / - 0.1 VDC
Total rated output voltage: + 5 + / - 0.2 Vdc
Short-term maximum output current: P 1000 mA
Maximum output current for a long time: 600 mA
Ripple Output Level: 50 mV or less

The declared 3W / 5C = 0.6 A power supply can only give a drawdown of up to 4.85 V, while it heats up to a temperature of 43 degrees. In general, good power sources are obtained for a small price.
Cost: ~ 139